
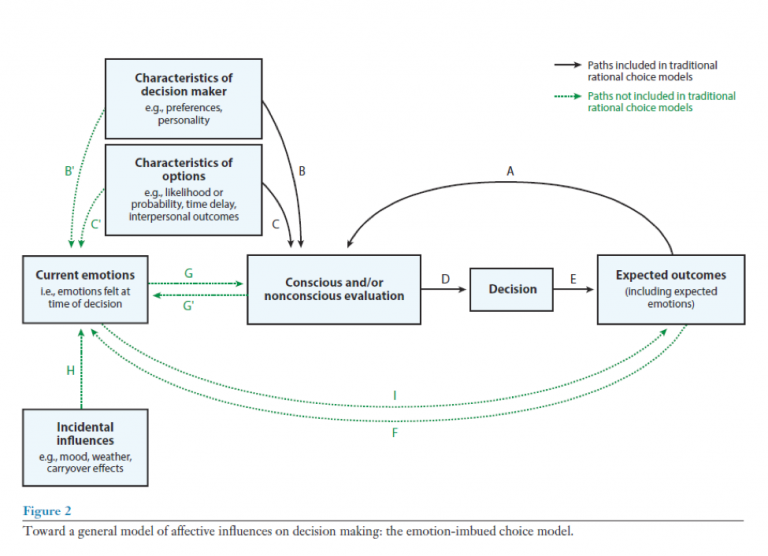
Davis ranks applicants by the disadvantages they have faced. It presents various essays on behavioral economics and behavioral finance that draw on the theory of Black Swans (Taleb 2010), which argues for a distinction between unprecedented events in our past and unpredictable events in our future. These results are discussed in light of neural developmental trajectories observed in adolescence. With End of Affirmative Action, a Push for a New Tool: Adversity Scores To build a diverse class of students, the medical school at U.C. This book is an exploration of the ubiquity of ambiguity in decision-making under uncertainty. Intuition is a perfectly acceptable means of making a decision, although it is generally more appropriate when the decision is of a simple nature or needs to be made quickly. Performance on the affective task was not related to performance on the cognitive task. It can, however, ignore emotional aspects to the decision, and in particular, issues from the past that may affect the way that the decision is implemented. Results indicated that in the affective task, adolescents performed sub-optimally by considering only the frequency of loss, whereas in the cognitive task adolescents used relatively mature decision rules by considering two or all three choice dimensions. Both tasks required a comparison of choice dimensions characterized by frequency of loss, amount of loss, and constant gain. It is not a personality trait, but a habit-based propensity to react in a certain way in a specific decision context» 1. In this study we compared adolescents' (13-15 years) performance on matched affective and cognitive decision-making tasks, in order to determine (1) their performance level on each task and (2) whether performance on the cognitive task was associated with performance on the affective task. Decision-making is a central part of daily interactions it was defined by Scott and Bruce in 1995 as «the learned habitual response pattern exhibited by an individual when confronted with a decision situation. Affective forecasting, also known as hedonic forecasting, refers to predictions of how we will feel about future emotional events.1.

Adolescents demonstrate impaired decision-making in emotionally arousing situations, yet they appear to exhibit relatively mature decision-making skills in predominantly cognitive, low-arousal situations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
